Virtualization with Hyper-V – Know the basics
Hyper-V Terminology
Term |
Functionality |
| Windows Hypervisor | Windows Hypervisor is a software interface that sits between the physical hardware and one or more Operating Systems. It controls access to a core set of hardware and guarantees isolation between the partitions, enforces policy restrictions for hardware access, and monitors the partitions. |
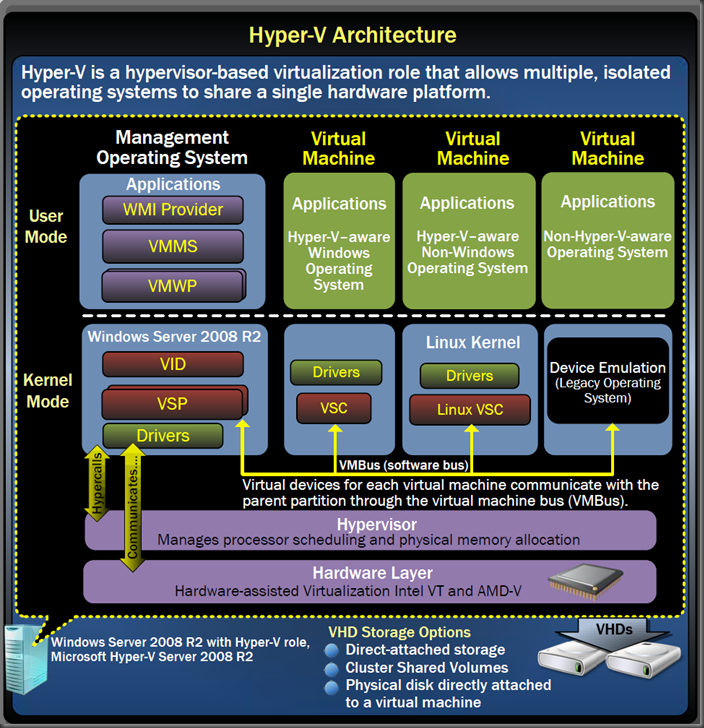
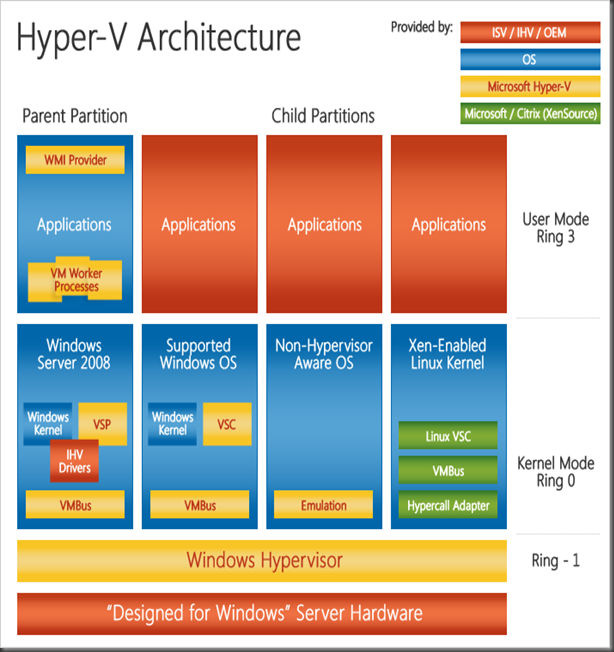
| Partitions | Partitions are containers isolated from each other by Hypervisor. A partition consists of Virtual memory address space, one or more virtual processors, worker processes, and communication interfaces. The virtual memory address pace of a partition is mapped to the physical memory address space of the physical server. There are two types of partitions in Hyper-V: Parent and Child. Hyper-V contains one parent partition and one or more child partitions. |
| Parent Partition | Parent partition is the first partition that is created. Although it is technically a virtual machine, it has unique features. It owns all of the resources not owned by the hypervisor. It manages the creation and operations of the child partitions.It controls access to the shared resources and defines whether they can be shared by the child partitions or are restricted to a single child partition. It is in-charge of power management, plug-and-play, and hardware events.Whereas a child partition sees emulated or synthetic devices, the parent partition sees the real hardware. |
| Child Partition | Child partitions are software-based representations of physical hardware and are also referred to as Virtual Machines. They have no direct access to the real physical hardware of the server. Each child partition sees the same exact base virtual hardware: motherboard, serial ports, video card, PCI bus, and so on and additional hardware can be “plugged into” the virtual motherboard.These include, virtual network adaptor cards, virtual SCSI adaptors, virtual hard disks, virtual CD/DVD drives and memory. |
| Virtualization Stack | The Hyper-V virtualization stack is a collection of software components and virtual devices that work together to support the creation and management of virtual machines. There are components of the stack that work in parent and the child partitions. The virtualization stack includes the following major components: -Worker process -Configuration Component -Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) Interfaces -Virtual Machine Management (VMM) Service -Virtualization Service Provider (VSP) -Virtualization Service Clients (VSC) -Virtualization Interface Driver (VID) -Virtual Stack Memory Manager (VSMM) -Virtual Machine Bus (VMBus) -Emulated Devices -Virtual Motherboard -Integration Services |
| Virtual Machine Management Service (VMMS) | It is a collection of components that work together to manage virtual machines. It is implemented as a single executable service module, VMMS.exe, under the name Hyper-V Virtual Machine Management. (This is different from System Center Virtual Machine Management service). The Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) maintains a list of virtual machines defined in Hyper-V, creates worker processes, manages the Virtual Machine configuration and addition or removal of devices. |
| Configuration Component | The configuration component provides the creation, management, modification and destruction of child partition configuration settings. Configuration settings are stored in an XML file. By default, the configuration file is created at the root of the directory where the virtual machine is created and assigned the filename GUID.xml, where GUID is the Globally Unique identifier of the child partition. |
| Virtualization Service Providers (VSPs) | These are software components that run in the parent partition and handle Input/Output (I/O) requests on behalf of the virtual machines. VSPs provide the interface via the VMBus to Virtualization Service Clients (VSCs). VSPs also communicate to the physical hardware, via the Windows Driver stack or device driver, to handle I/O requests. |
| Virtualization Service Clients (VSCs) | These are synthetic drivers that run within the child partition and communicate across VMBus to corresponding service Virtualization Service Providers in the parent partition. |
| VMBus | VMBus is a high-speed interpartition communications mechanism that is made up of multiple components or technologies. VMBus is designed to provide point-to-point communications between child partition and parent partition over a dedicated channel. Each VSP provides a dedicated channel for child partition VSC. A single VSP can communicate with multiple VSCs. |
| Virtualization Infrastructure Driver (VID) | It is the parent partition kernel level interface to the Windows Hypervisor using defined API interfaces called hypercalls. The VID provides service to the worker and administrative management interface running in the user mode and communicates with Windows Hypervisor to coordinate execution of Virtual Machines. |
| WMI Interfaces | WMI Interfaces exist to allow for the remote management and operations of Hyper-V. WMI Interfaces consist of WMI service, WMI clients and WMI providers. The Hyper-V Virtual Management Service (VMM) implements the primary providers that allow the management of child partitions. |
| Worker Process | A Worker process is created for every virtual machine that is running or being configured. The job of the worker process is to manage the running state of the virtual machine and its devices, manage remote RDP sessions, and communicate with the integration services running in the child partitions. |
Technorati Tags: Hyper-V,Windows Server 2008,R2,virtualization,architecture