Intelligent ERP: Using data and analytics to improve business processes and operations

Enterprise resource planning applications have been around for few decades now. What started in the 1980s as materials requirement planning for specific business operational areas became enterprise resource planning in the 1990s. The business driver for ERP applications was the concept of conducting business by standardizing business processes, so that operational applications for managing those processes could also be standardized.
These applications provided a faster way to deliver business operational applications, and soon became integral to many organizations. Operational data from various sources could be entered and loaded into ERP applications, and those became the single source of truth for operational data. The success of ERP applications depends on the quality and depth of entered data. Deeper, more minute data related to different business operations provide visibility of business functionality to end users.
Integrating Microsoft IoT
Adding data captured by integrating Microsoft Internet of Things increases what customers can learn about optimizing their operations. Sensors and devices can capture data at various points of operations and supplement other operational data to provide valuable insights. Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Field Service allows smart products to report service issues or other problems themselves.
For example, a food supply company can have sensors that provide the temperature of cooler when a shipment is dispatched to ensure product quality, and can also use sensors to provide information about shelf life of perishable items to help with raw material usage. The list of possibilities for adding data points that lead to better business insights about how valuable resources are applied is long.
Applying machine learning
Machine learning algorithms, used to capture information and adjust business processes, also provide a rich dimension of operational data useful in enterprise resource planning. Users of both Microsoft Dynamics CRM and Microsoft Dynamics ERP are good candidates for using machine learning to improve the way their businesses run. Azure Machine Learning is a simple, scalable service that lets you build predictive analytics solutions to obtain valuable information underlying operations so that business processes can be adjusted.
Explore the Azure Machine Learning resources - introduction for technical professionals, documentation, tutorials, gallery, and more - to learn how you can add recommendation and prediction engines to improve performance and decision-making in existing business processes like e-commerce, customer service, demand forecasting, and more.
Azure Machine Learning and Azure IoT Hub can be differentiators for sourcing data to ERP applications like Microsoft Dynamics 365. Integrating Azure IoT Hub and Azure Machine Learning data with an ERP application helps provide the extra level of intelligence to business operations that are not available elsewhere. Data collected from IoT-enabled devices and sensors can be parsed to identify business relevant data inside Azure IoT Hub and then uploaded into Microsoft Dynamics 365. It is faster, cheaper, and provides better quality data with low latency.
Cortana Intelligence Suite
The Microsoft Cloud Platform includes services offering machine learning algorithms that use data from multiple sources to get an understanding of the underlying operations. Both enterprise resource planning and customer relationship management benefit from the integration of data gathered through machine learning and the internet of things. The data can be further enhanced with cognitive analysis, using Cortana Intelligence Suite.
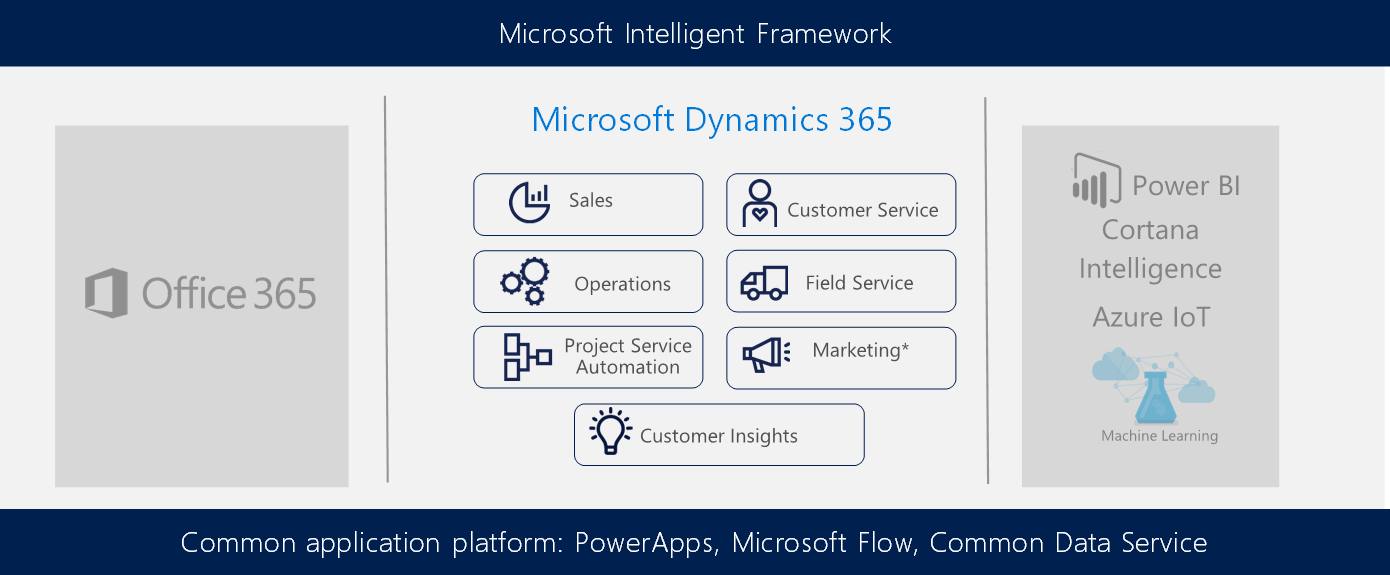
As an example, sentiment analysis is a common customer satisfaction measurement. It's typically performed through keyword recognition. Using cognitive analysis in Cortana Intelligence Suite and the Microsoft Bot Framework, you can get a more rounded view of customer sentiment, adding data from call logs, email responses, and other datasets. This functionality can be integrated with Microsoft Dynamics CRM to provide an additional level of intelligence.
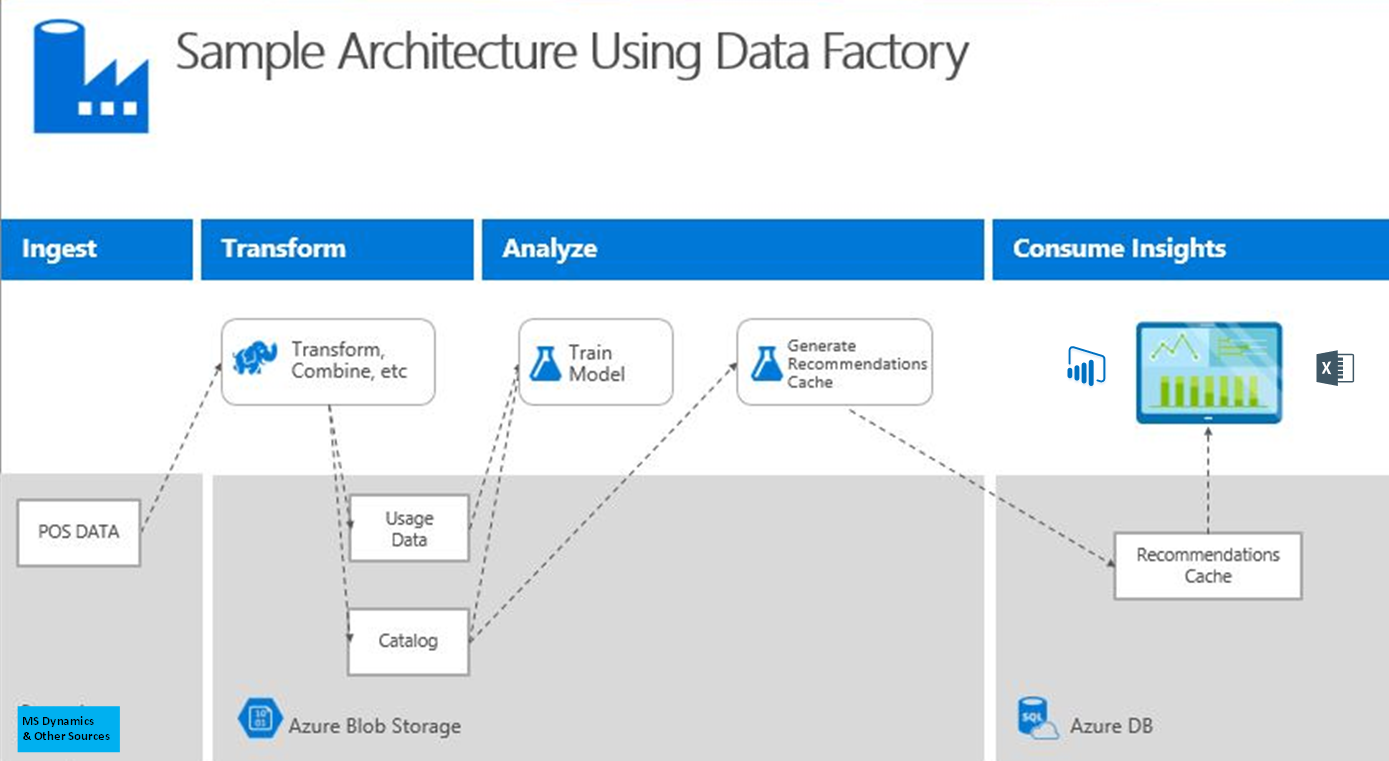
Integration of enterprise data from ERP applications and other operational and analytic applications used by an organization is a requirement for business analytics. Azure Data Factory, which lets you orchestrate and manage data movement and transformation, can be hooked up with Microsoft Dynamics 365 to gather operational data for analytics. These data can be merged with other internal and external data from an organization. Azure Data Factory has built-in connectors for varied data sources including relational data sources, social platforms, and other structured and unstructured data sources. Upload data to Azure Data Lake Store or Azure SQL Data Warehouse for analytics. Customers can then view their data using Microsoft Power BI reporting and dashboards.
The partner opportunity
Microsoft Dynamics 365 with Azure IoT, Azure Machine Learning, and other Microsoft Azure intelligence and analytics products and services can help you build and sell solutions that meet customer requirements for data capture, business operations, and analytics. An end-to-end delivery of this solution stack can increase deal sizes and establish longer-term relationships with the customer - these offerings focus on business value and can lead to discussions that go beyond technology. For more information about intelligent enterprise resource planning use cases, visit the Cortana Intelligence Gallery and the Microsoft Dynamics 365 website.